DSL vs Satellite Internet: Best Rural Internet Options
Table of Contents
High-speed internet access is the key to opportunity in many rural areas. If you have an internet connection, you can get remote work or pursue education in almost any career field.
But if you live in less-populated parts of America, your rural internet options will often be limited. Fiber internet and cable internet are not available in many parts of the country.
That’s why the federal government has committed to expanding internet infrastructure for the American public with over $20 billion in the Rural Digital Opportunity Act.
Until more infrastructure is built, your choice for rural internet is often going to come down to DSL vs. satellite internet.
Understand your satellite and DSL internet choices
In this guide, we’ll take you through everything you need to know about DSL and satellite internet to choose your best home internet service provider.
First, we’ll explain how each technology works. You’ll learn why DSL and satellite internet are available to rural and remote areas when other types of internet are not. Then we’ll go through internet speeds, latency, and pricing to help you compare all the factors.
How DSL Internet Works
DSL internet (from “Digital Subscriber Line") runs through copper wiring that also carries landline telephone signals. In the 1990s, DSL providers were offering DSL as a popular new alternative to dial-up internet service.
At that time, DSL internet was 10 to 100 times faster than dial-up internet. What’s more, DSL allowed customers to use the internet without any interruptions from their phone. People over the age of 45 will remember the days when dial-up internet meant you lost your internet connection every time the phone rang!
With DSL, internet data transmits on different frequencies than voice telephone calls, even though the signals pass through the same phone line. Those different frequencies give DSL the ability to provide both internet access and phone service simultaneously.
The fact that DSL connections work through phone lines is why rural areas often have DSL providers even when they do not have cable or fiber infrastructure.

How Satellite Internet Works
Satellite internet connections have three major parts.
1) your satellite equipment at your home, including satellite dish, modem, and computer
2) a satellite orbiting Earth, owned by one of the major satellite internet providers
3) A ground station constructed by your satellite internet provider and hardwired into the internet
Satellite service happens when you make an internet request on your computer. That request beams from your home satellite dish to the satellite out in space. The satellite beams it back down to the ground station of your satellite internet provider. Their hardwired connection retrieves your data from the internet.
The satellite provider’s ground station sends your requested internet data back through space to their satellite, which beams it back down to earth to your receiver satellite dish. Your dish then sends that information through your modem to your computer.
It’s truly a tech marvel that a satellite so far out in space can “catch" a specific internet signal from the ground station and “throw" it to your home across an equal distance. Satellite connection has for many years been the only type of internet connection that can be reliable almost anywhere in the world.
Far Out, Man! How Far Out is Your Satellite?
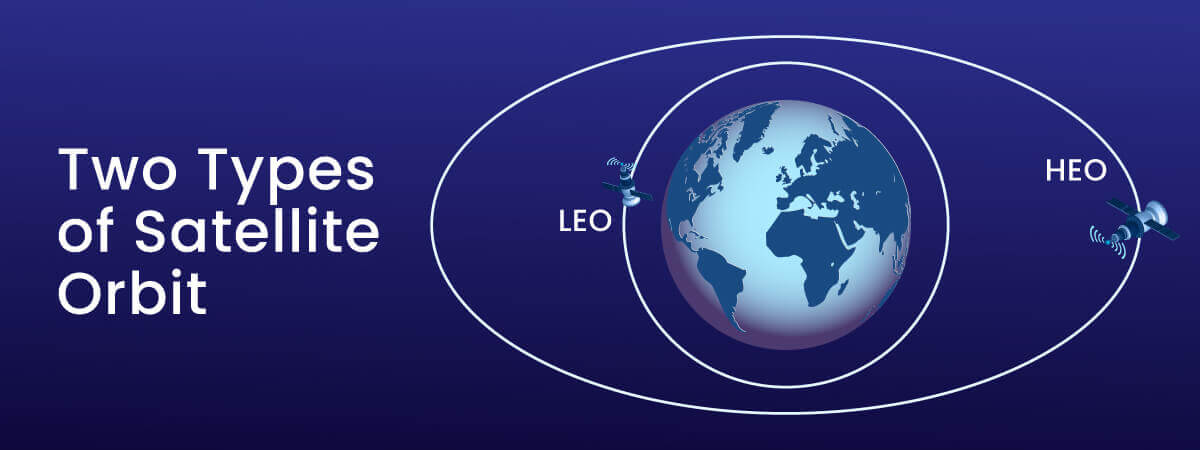
Satellites providing internet will fly in one of two types of orbit: High-Earth Orbit (HEO) or Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
HEO satellites remain in one place above the earth because they travel at the same speed as the earth’s rotation. One satellite can maintain a steady connection with your satellite receiver at all times.
LEO satellites are only 155 to 2000 miles above the surface of Earth. They do not maintain a constant position above one point on earth because they orbit very fast, circling the earth in only 90 minutes. An LEO satellite internet provider must keep a cluster of satellites orbiting at the same time to keep your satellite internet connection when one satellite flies out of your range.
Major satellite internet providers include Viasat, Viasat, and newcomer Starlink.
Viasat uses HEO satellites that stay in one place above the earth, which are known as geosynchronous satellites. Viasat also uses geosynchronous satellites to provide satellite internet connectivity.
Starlink, a newer company started by Elon Musk’s SpaceX, is launching LEO satellites.
Understanding Internet Speeds in DSL and Satellite Internet Services
Almost all satellite internet providers and DSL internet providers offer an internet connection with what is called “asymmetrical speed." Asymmetrical means uneven. That means your download speed will be much faster than your upload speed.
There’s a lot of debate these days about whether all internet connections should be striving for symmetrical broadband that has the same speeds for its downloads and uploads. Right now, fiber internet is the only technology that provides symmetrical speeds to large numbers of customers.
Though symmetrical speeds have definite advantages, some nonprofit groups argue that symmetrical speed is not necessary for most internet users.
That’s good news if your only choices right now are DSL and satellite internet.
How much internet speed do you need?
The FCC defines broadband internet speed as 25 Mbps download speed/3 Mbps upload speed. That is an asymmetrical speed or what you might call a “one-way fast, one-way slow" internet connection.
It’s quite possible that “one-way fast" broadband download speed will be enough to handle all of your internet needs. Many people are most interested in internet activities based on downloading, such as web and social media browsing. If that’s what you usually do on the internet, only your download speeds will matter.
 When do you need faster speeds for uploading? When you are sending large files of your own or uploading them to websites. For example, if you are someone who works with video or image design, you will need faster upload speeds to avoid timing out during your uploads.
When do you need faster speeds for uploading? When you are sending large files of your own or uploading them to websites. For example, if you are someone who works with video or image design, you will need faster upload speeds to avoid timing out during your uploads.
Upload speeds also matter when you are playing real-time multiplayer games or videoconferencing for work. Faster upload speeds will prevent glitches and screen hangs.
Latency: the stealth factor in internet speeds
There’s one last thing you need to know about internet speed to understand your choice of DSL vs. satellite internet.
Latency is a delay in an internet signal that happens when a signal travels a long distance. Some speed tests refer to latency as your “ping time." So, even if you have high-speed internet, high latency may affect how quickly your computer receives responses.
If you mostly use your internet connection to send emails and browse the web, you may not ever notice higher latency.
Satellite internet is known for higher latency than other types of internet connection, simply because satellites are so much farther from your home than other transmitting sources.
However, keep in mind that DSL can also vary in latency depending on its distance from a central server. For the most part, though, DSL will have much lower latency than satellite.
One satellite internet provider has been working to create a low-latency satellite internet connection. Viasat Fusion uses hybrid technology to combine satellite and wireless transmissions. This lower-latency connection is now available in select areas, and might be a solution for your DSL vs. satellite decision.
Average satellite internet speeds vs. average DSL speeds
DSL internet varies in its speed, so you will need to know the speeds available from your local internet service providers. The Pew Trust estimates DSL speed as follows: a single telephone wire will deliver speeds up to 24 MBPS, while a pair of bonded sets of wires can deliver speeds of up to 48 Mbps.
Buyer beware, however, when you see the words “up to" 24 Mbps. You will notice that “up to" phrasing is standard for internet service providers. Your actual DSL speed might be much slower.
DSL speeds: advertised vs. actual
The FCC’s Measuring Broadband America Eleventh Report found that advertised speeds for DSL are usually much lower than the 100 Mbps sometimes claimed for newer DSL, hovering at a mean speed of about 21 Mbps. Even more concerning is the fact that the same report found that DSL internet providers tended to fall short of their advertised speeds, while other types of internet providers regularly exceeded their advertised speeds.
What all of this tells you: DSL speeds may be a lot slower than your provider implies. So much depends on the technology available at your home. So talk to your neighbors. Ask them if they’ve done a speed test on their DSL connection. That will give you a more realistic idea of your potential DSL speed. You don’t want to sign up for an advertised download speed of “up to 30 Mbps" and find out that it’s actually 6 or 7 Mbps once your DSL service starts.

Satellite Internet Speeds
In 2017, Viasat was the first satellite company to offer high-speed internet according to the FCC’s definition, at 25 Mbps/3Mpps. Viasat has consistently earned top marks from the FCC for exceeding its advertised speeds.
Another advantage of Viasat’s satellite internet speeds is their consistency. Viasat offers the same speed to customers across the USA, no matter what their location. The company has also announced that its Jupiter 3 satellite launch in 2023 will enable even higher download speeds of 100 Mbps or more.
Viasat offer satellite internet speeds that can be higher (up to 100 Mbps download) but also lower (12 Mbps download). This difference is significant, so you should know that speed may vary according to your location.
Starlink, a newer satellite service from Elon Musk’s Space X, provides fast speeds from 50 -500 Mbps. Starlink is more expensive than the two established providers. Starlink is also not yet available in many areas and has waitlists for service.
Pricing: DSL vs Satellite Internet
On the whole, you will find that pricing is more expensive for satellite internet than for DSL internet.
Basic monthly plan fees may start at similar rates at about $50/month with the promotional rates offered by Viasat, for example. (After six months, the first-tier plans will resume the standard rate of $70/month.)
DSL plans from major providers such as CenturyLink also tend to start at around $50/month, depending on your location. The price difference is that with DSL, you will not have to purchase or rent equipment. However, satellite equipment rental fees tend to run only $10-15 a month. So if you’re not ready to invest a few hundred dollars up front in a satellite dish and modem, you can rent at a reasonable fee.

Satellite Internet Data Allowances
The other major difference between DSL internet and satellite internet is how the different internet providers handle data.
Satellite internet providers have a certain amount of bandwidth for all their customers. This means they have to ration your data usage to make sure that all their customers get fair access to data.
Though satellite internet providers will often claim “unlimited data," what that phrase actually means is soft data caps. Viasat, for example, will not cut off your internet access if you exceed your monthly data cap. Instead, your internet will slow down significantly. You can then buy a Data Token to expand your data for that month if necessary.
If you choose satellite service, you will want to read the fine print on your data allowances. The advantage of a data plan with soft caps such as Viasat’s is that you will know exactly what you are spending at all times. Some ISPs may instead charge you data overage fees, which can be an unpleasant surprise on your monthly bill.
Pros and Cons of Satellite Internet Service
| PROS | CONS |
|
|
Pros and Cons of DSL Internet Service
| PROS | CONS |
|
|


